FORESTATION IN INDONESIA
-
Forest in areas with specific physical characteristics that warrant protection to sustain particular functions, especially with respect to hydrology and soil conservation.³⁴
-
They serve not only to protect and preserve genetic resources and life supporting systems but also to provide materials for the development of science and education. ³⁴
-
Production forest is designated for exploitation of timber, rattan, sap and other forest products.
Limited Production (23.06 Mha)
Permanent Production (35.2 Mha)
Limited production forest is designated for prevention of soil erosion as well as timber production. Under the forestry rule, trees with diameter at breast height of >60 cm may be felled whereas in permanent production forests the cutting limit is 50 cm. ³⁴
Causes of Deforestation
Slowing deforestation rates in Indonesia were linked to a drop in the market value of crude palm oil ³⁹
The loss of many tropical forests are mostly man-made:
Illegal logging for wood products as raw material for wood pulp and paper industry.
Converting forest land to palm oil plantations
Oil palm was responsible for one-third of Indonesia’s loss of old-growth forests (9.79 million hectares cleared, or 11 percent of forest area in 2000) over the last two decades. ³⁸Burning of forests by large-scale corporations
*not to be confused with slash and burn which is a rotational farming method used by small-scale farmers and tribes
Primary forest loss and its related cause. ⁴⁰
Land Use Characteristics ⁴²
-
482.393 sq km
85 people / sq km
23 million ha of forest land (47.1 % of total land area)Dominant land use: 80 % of the population are farmers practicing shifting cultivation and managing rubber and oil palm plantations.
Forest management: Sustainable forest management not yet introduced on a largescale; large tracts of land are unproductive grasslands and degraded secondary forests, particularly in South Sumatra and Lampung.
-
127.499 sq km
910 people / sq km
3 million ha of forest land (23 % of total land area) mostly protection forestsDominant land use: 65 % of the population are farmers with only 0.2 ha agricultural land per family. Traditional home gardens developed over time represent an important element in integrated farming systems.
Forest management: High social pressure on forests due to increasing population density
-
547.891 sq km
20 people / sq km
37 million ha of forest land (66,9 % of the total land area) dominated by
dipterocarp forests (hardwood trees).Dominant land use: Forestry and increasingly oil palm, rubber and timber plantations
Forest management: Forest conditions rapidly deteriorate due to fire and land clearing; sustainable forest management not yet introduced on a arge-scale; large tracts of land are unproductive grasslands and degraded secondary forests.
-
191.800 sq km
72 people / sq km
12 million ha of forest land(62.7% of total land area)Dominant land use: Farming area mostly rice cultivation in the South; however, several of those areas are hilly.
Forest management: -
-
87.744 sq km
125 people / sq km
3.4 million ha of forest land (38.3 % of total land area)Dominant land use: Pasture management and agroforestry systems well developed.
Forest management: -
-
77.871 sq km
26 people / sq km
5 million ha of forest land (62,8 % of total land area) -
421.981 sq km
6 people / sq km
28,8 million ha (68,3 % of total land area)
Dominant land use: Several large-scale mining projects for gold, oil and other minerals are also found in this area.Forest management: -
The amount of time taken for forest land to recover after deforestation⁴¹.
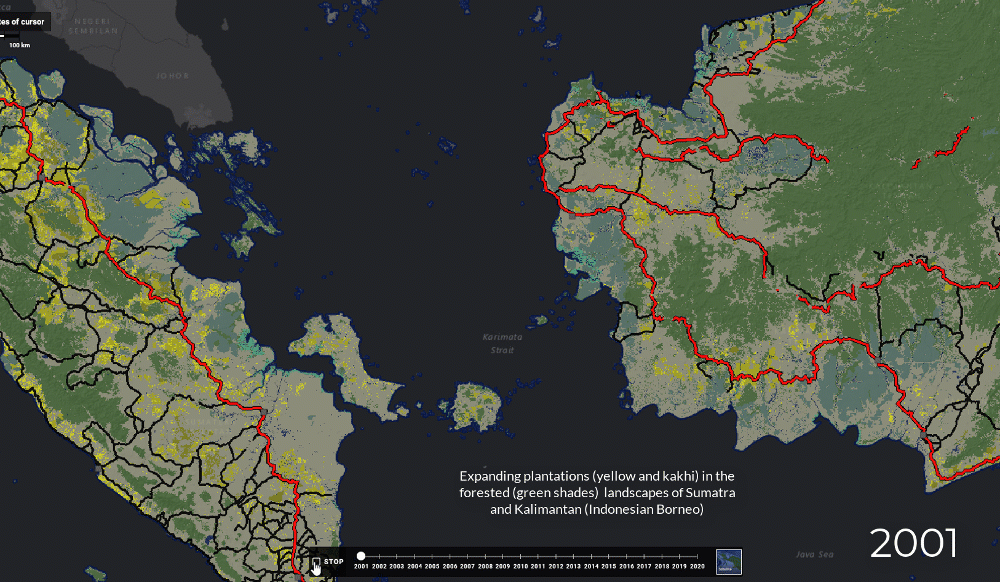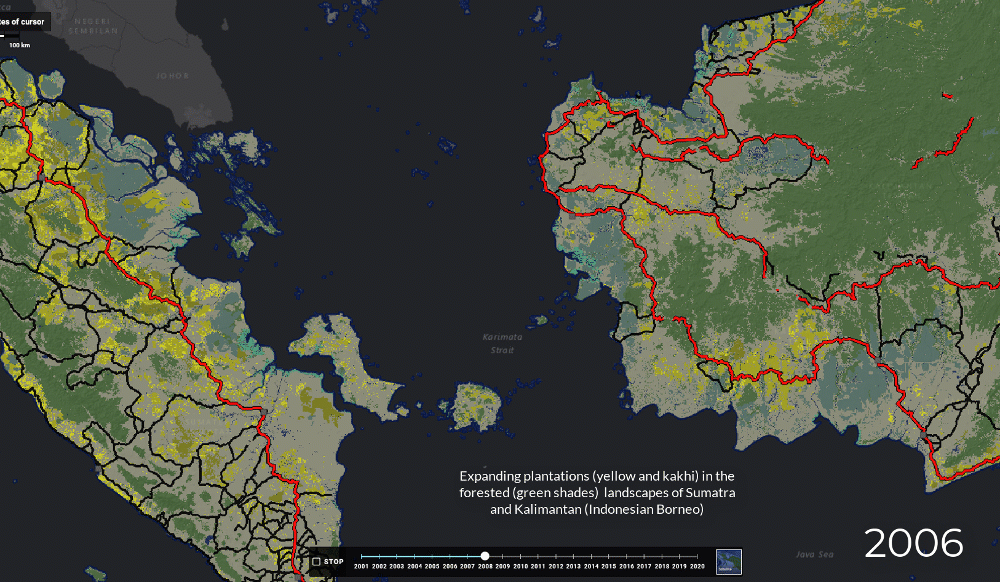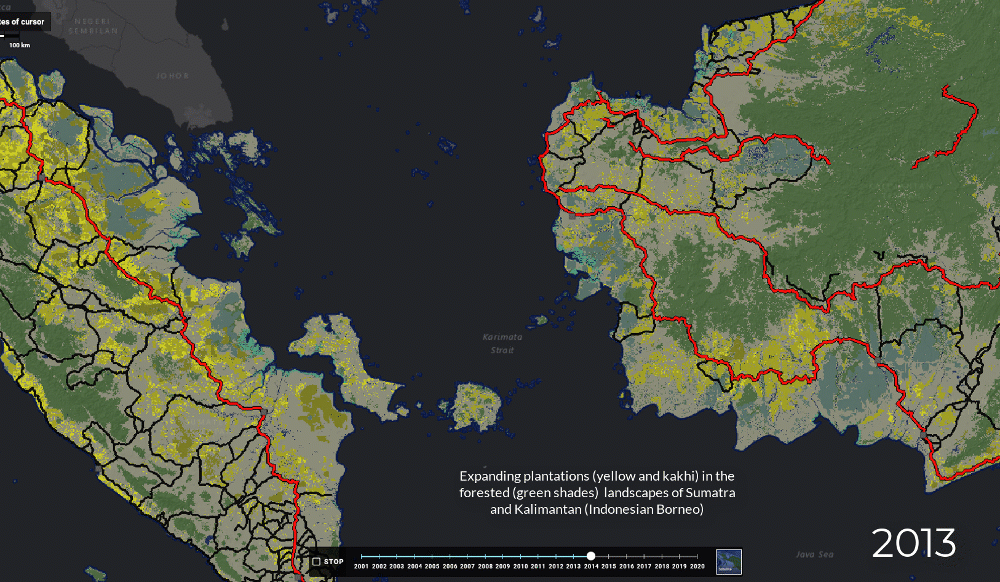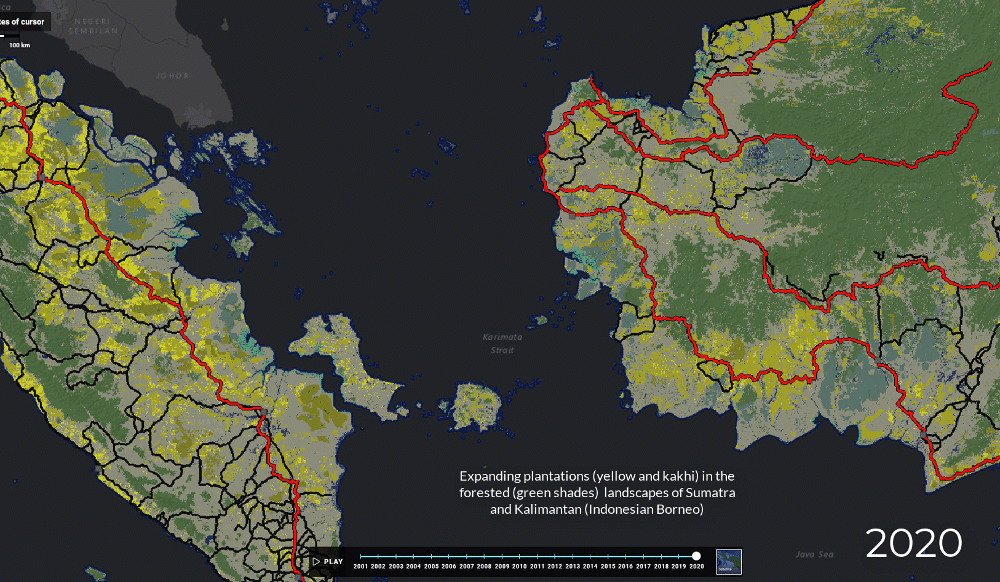
Map of Indonesian forest exploitation and degradation, 2000 - 2012 ³⁶